With the release of Apache StreamPipes 0.97.0, the OPC UA adapter now supports encrypted communication using certificates, enhancing security for Industrial IoT applications. This guide walks you through generating certificates, configuring them in StreamPipes, and setting up your OPC UA server for secure communication.
Introduction
While an unencrypted security policy is the way most users try when they start testing StreamPipes for their first time, production-grade scenarios typically require encrypted communication.
In case you are already using Apache StreamPipes, you might have noticed that the OPC UA adapter now supports encrypted security policies:
In this guide, I'll show how to set up a secure connection between your OPC UA server and Apache StreamPipes. This guide is intended to be a step-by-step-guide starting from certificate generation to the configuration of the OPC UA adapter in StreamPipes.
I'll show a working example on a local installation using Eclipse Milo as the OPC UA server. The same steps can be applied to production systems by integrating certificates into the volume of the extension service. There are other ways to configure OPC-UA secure connections, but this guide will focus on a complete approach using self-signed certificates for beginners.
Prerequisites
- Apache StreamPipes 0.97.0 or newer
- An OPC-UA server supporting security policies
SignandSign & Encrypt - OpenSSL installed on your system
Generate client certificates
When creating a new OPC-UA adapter in Apache StreamPipes, the extension service where the adapter is running in serves as the client. First, we need to create a client certificate for the client. In this example, we'll create a self-signed certificate.
[req]
default_bits = 2048
prompt = no
default_md = sha256
req_extensions = req_ext
x509_extensions = v3_ca
distinguished_name = dn
[dn]
CN = stream-pipes-client
[req_ext]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment, keyCertSign
extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth, clientAuth
[v3_ca]
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
basicConstraints = CA:false
subjectAltName = @alt_names
keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment, keyCertSign
extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth, clientAuth
[alt_names]
URI.1 = urn:org:apache:streampipes:opcua:client
When using a self-signed certificate, it is requried to to provide the CA:false flag under basicConstraints. In addition, note the subject alternative name that later needs to be matched by the application URI of the OPC-UA client.
The next step is to generate the certificate and import it into a PKCS12 keystore. The keystore is used to store the key pair we are generating in the first step.
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 \
-newkey rsa:2048 \
-keyout client.key \
-out client.crt \
-config cert.conf \
&& openssl pkcs12 -export \
-in client.crt \
-inkey client.key \
-out client.p12 \
-name streampipes-client
When I was asked for a password, I chose streampipes. You can choose any password you like, but make sure to remember
it, as
we will need it in the next step.
Check that the keystore lists the correct key by executing:
keytool -list -v -storetype PKCS12 -keystore client.p12
You'll see the key you've just generated.
Configure StreamPipes to support encrypted connections
To enable the OPC UA adapter to use the generated client certificate, we need to provide a few environment variables to StreamPipes.
Here is a list of all environment variables that are available:
- SP_OPCUA_SECURITY_DIR (default: /streampipes-security/opcua): This is the directory where the keystore and trusted/rejected server certificates are stored.
- SP_OPCUA_KEYSTORE_FILE (default: keystore.pfx): This is the keystore file that contains the client certificate.
- SP_OPCUA_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD (default: password): The password for the keystore file.
- SP_OPCUA_KEYSTORE_TYPE (default: PKCS12): The type of the keystore file.
- SP_OPCUA_KEYSTORE_ALIAS (default: apache-streampipes): The alias of the client certificate in the keystore.
- SP_OPCUA_APPLICATION_URI (default: urn:org:apache:streampipes:opcua:client): The application URI of the client certificate.
We could have made the previous configuration easier by reusing some of the defaults. For learning purposes, we used some other names for the alias and keystore filename.
In my setup, I've started a local StreamPipes instance. When using Docker, you can add the environment variables to the extensions service (e.g., extensions-all-iiot). In my local instance, I just add the emnvironment variables to my IDE settings.
I add the following variables:
SP_OPCUA_SECURITY_DIR=/home/user/streampipes-security/opcua
SP_OPCUA_KEYSTORE_FILE=client.p12
SP_OPCUA_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD=streampipes
SP_OPCUA_KEYSTORE_ALIAS=streampipes-client
Connecting to an OPC-UA server
For this demo, I'm using the Eclipse Milo OPC UA server. You can download it from here. Once the server is running, you can connect to it using the following URL:
opc.tcp://localhost:62541/milo
Now it's time to switch to StreamPipes!
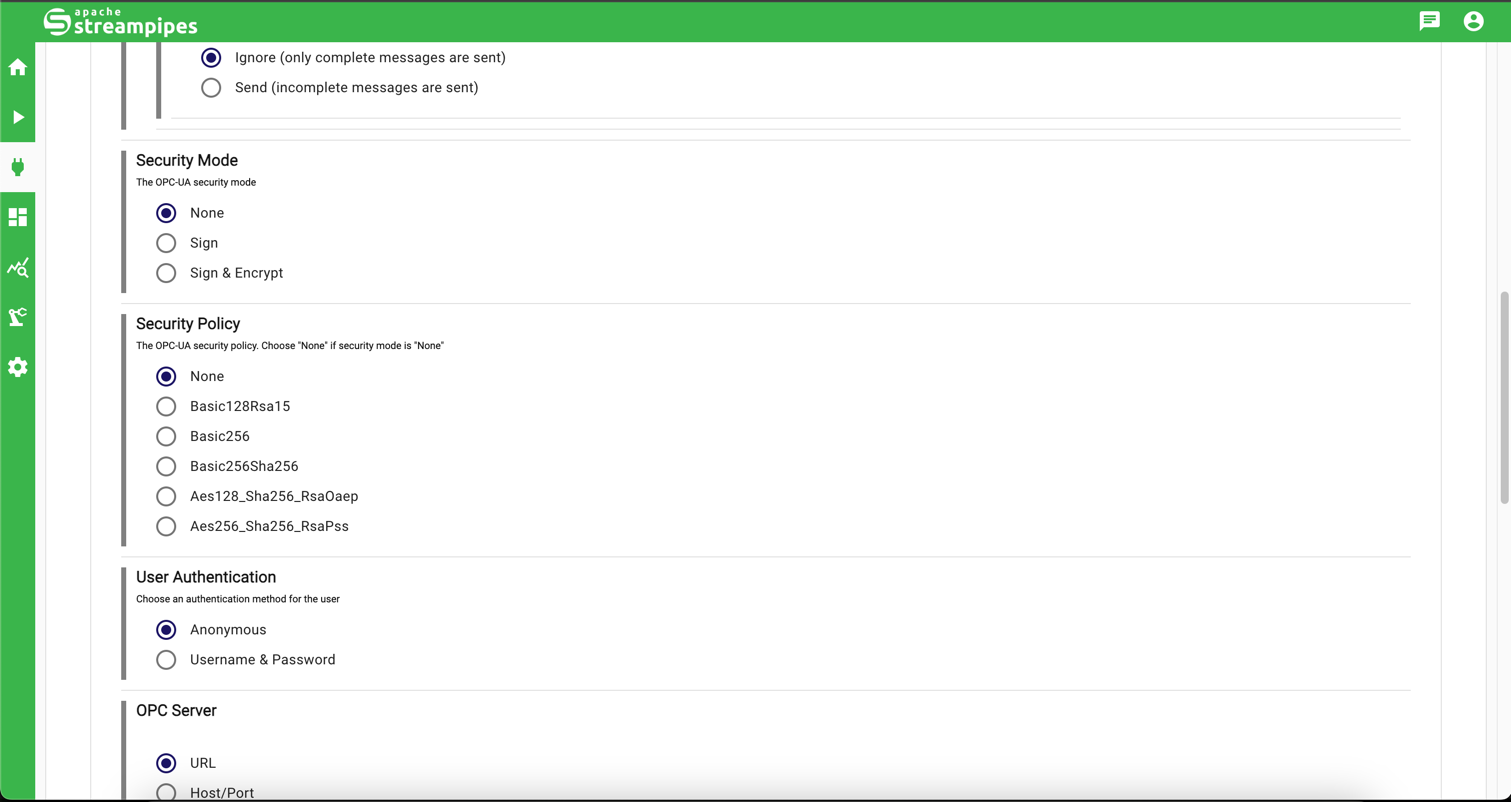
Go to Connect -> New adapter -> OPC UA and enter the following configuration:
Pull interval 1000
Incomplete Events Ignore
Security Mode Sign & Encrypt
Security Policy Basic256Sha256
URL opc.tcp://localhost:62541/milo
Defocus the URL input field and wait for the OPC-UA server to connect. After a few seconds, you should see an error message appearing:
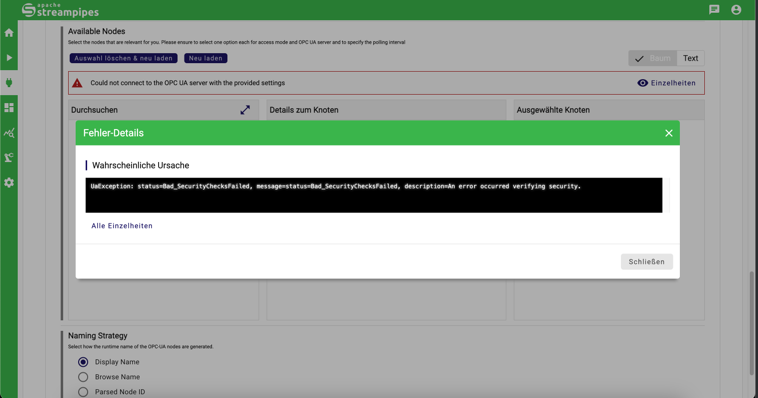
This is expected, as we haven't added the client certificate to the trusted certificates of the OPC-UA server yet.
So we have to let Milo know that the client certificate can be trusted. In my local setup, I need to move the client certificate from the rejected to the trusted/certs folder as seen below:
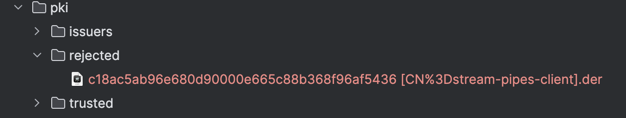
So let's try again by clicking Reload in the Available Nodes section of the adapter configuration page.
We'll get another error saying that the server certificate is not trusted.
This is again expected, as we haven't added the server certificate to the trusted certificates of the OPC-UA client yet.
To do that, we can have a look at the folder structure under SP_OPC_UA_SECURITY_DIR:
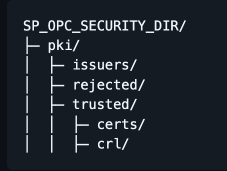
Several new folders have been created by the Apache StreamPipes OPC-UA client.
The trusted folder contains the trusted server certificates, while the rejected folder contains the rejected server certificates.
We'll move the server certificate from the rejected folder to the trusted/certs folder.
No we'll try again - and this time, we should see the available nodes in the adapter configuration page:
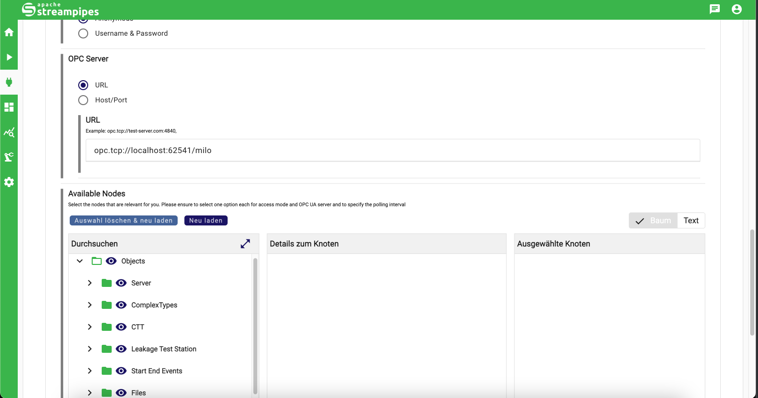
You'll see the beautiful tree view where you can navigate through all OPC-UA nodes.
Now you can select the nodes you want to use in your adapter.
That's it! You've successfully configured the OPC-UA adapter to use encrypted communication with self-signed certificates.
